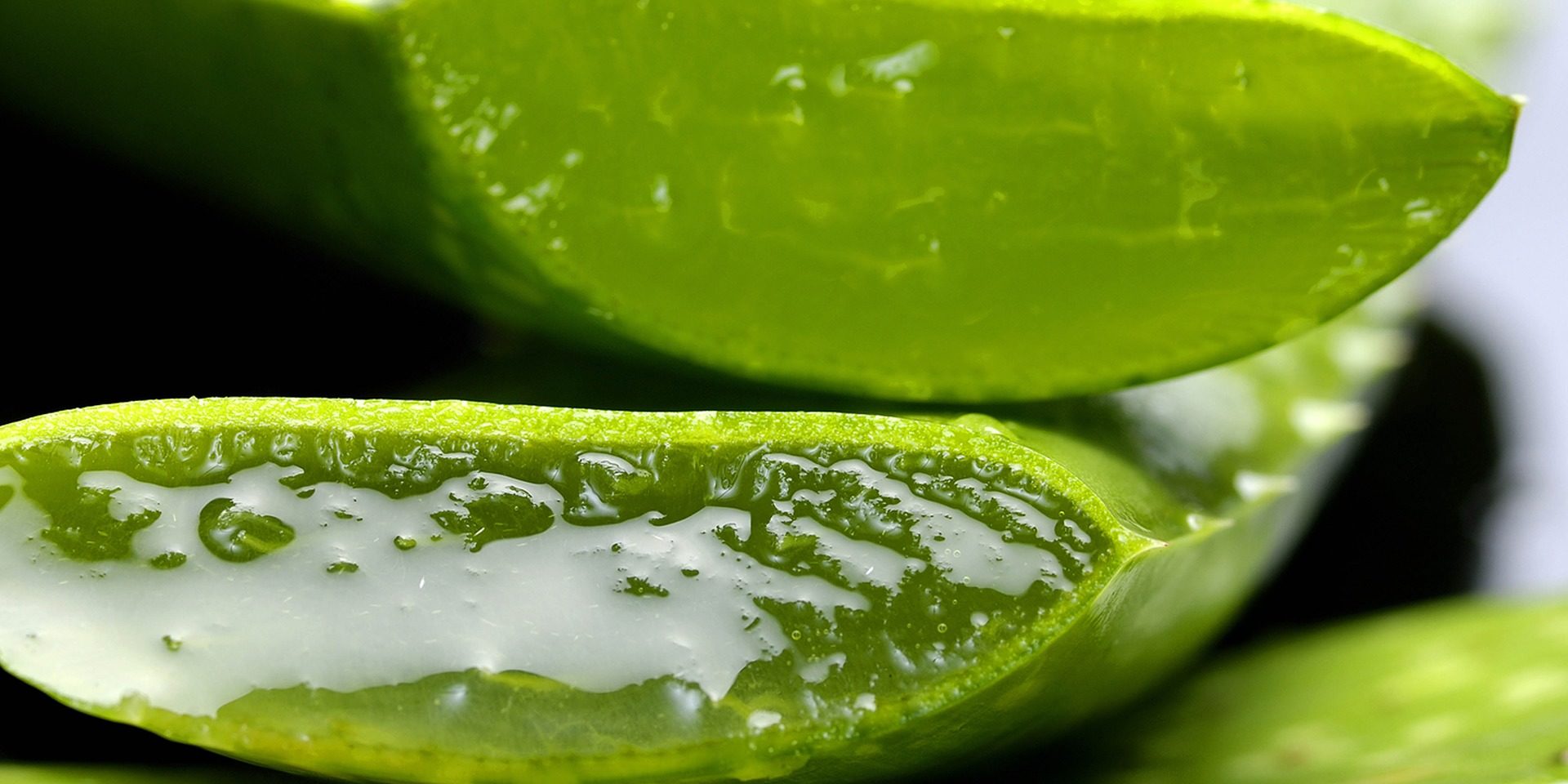
Aloe vera: botanical description and use
Aloe vera is a species belonging to the genus Aloe and to the family Asphodelaceae whose origin is still uncertain (GBIF site). This plant is mainly cultivated around the Mediterranean and in tropical countries. It has evergreen leaves that can measure from 20 to 30 cm in length and can reach a width of 10 cm. Its shallow roots form runners. Its flowering period extends over two seasons, in winter and spring. It forms inflorescences composed of yellow flowers. Its leaves, characteristic of xerophytic plants, are composed of several cell layers, including a mucilaginous aquiferous parenchyma from the inside to the outside, a lower wall (called the pulp) that contains the latex, and a cuticle (Figure 1). On a sheet, the pulp accounts for 70 to 80% and the cuticle for 20 to 30%. Found in arid environments, this succulent plant has the capacity to store water in its leaves, which can represent 98 to 99% of its weight (Moghaddasi S.M. and Kumar Verma S., 2011). It is also very rich in polysaccharides.
Since ancient times, Aloe vera has been widely used and is now one of the emblematic plants of the cosmetic and nutraceutical industries. This plant is known for its healing properties and is an essential ally for the skin. It can be used for its leaves, latex or gel. Its gel, composed of twenty mineral salts, eight essential amino acids and a dozen vitamins including vitamins A, B, C and E, is an ideal partner for health. Aloe vera can be used in the form of gel, juice, concentrate and leaf extract, found in many cosmetic products and food supplements.
 Figure 1: Aloe vera and its fleshy, thorny leaves. They are mainly made up of an aquiferous parenchyma that allows water storage.
Figure 1: Aloe vera and its fleshy, thorny leaves. They are mainly made up of an aquiferous parenchyma that allows water storage.
The techniques of DNA Gensee: DNA analyzed by barcoding and metabarcoding
Within the company DNA Gensee, an expert in plant genetics, two DNA-based genetic analysis techniques are used: barcoding and metabarcoding. Barcoding is a technique that uses long markers to identify plant raw materials using the Sanger sequencing method. Metabarcoding, complementary to barcoding, is used with short markers on lower quality DNA that can be degraded. Using the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) method, it is used to trace raw materials in processed products and to identify any adulterations/contaminations that may be present.
During a study, we analysed Aloe vera-based products. We identified samples down to species rank from raw materials with three of our genetic markers. We performed a metabarcoding analysis, where the results revealed an assignment to the genus Aloe.
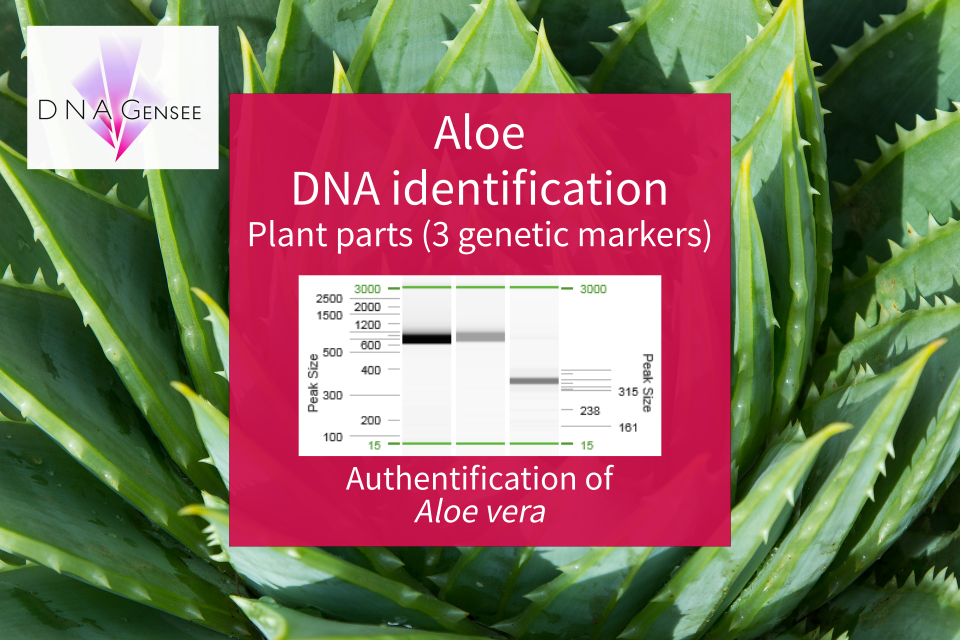 Figure 2: Expertise of DNA Gensee
Figure 2: Expertise of DNA Gensee
Conclusion
The advanced techniques used by DNA Gensee allow identification and authentication of plant raw materials and their traceability in the final products. These complementary techniques make it possible to deal with frauds and adulterations encountered particularly in the cosmetic field but also in the perfumery, nutraceutical and food industries, in order to guarantee transparency to consumers.
This study carried out on Aloe vera is an example of what can be done on other plant species.
References
Moghaddasi S. M, Kumar Verma S. 2011. Aloe vera their chemicals composition and applications : A review. International Journal of Biological & Medical Research. (2):1 : 466-471.
Sitography
https://www.gbif.org/species/2777724 https://www.lanzaloe.com/fr/blog/las-mentiras-de-la-industria-del-aloe-vera.html










